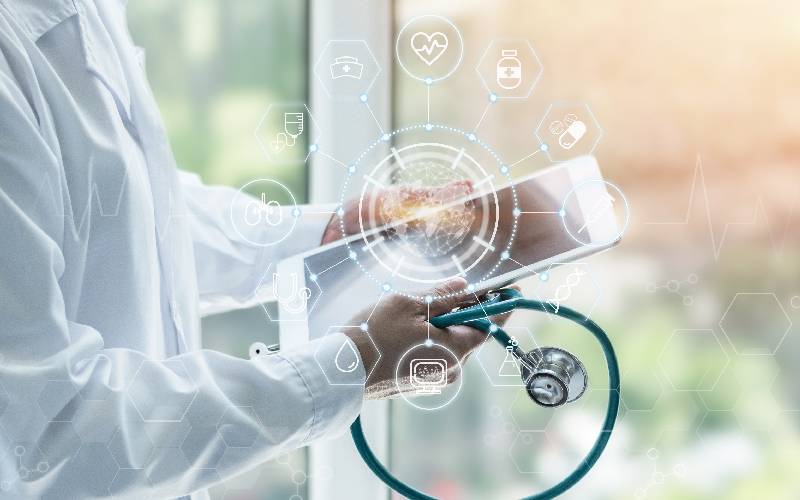
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a transformative force, redefining the way patients engage with their healthcare journey. Beyond its diagnostic and predictive capabilities, AI is playing a pivotal role in enhancing patient engagement, fostering a more proactive and personalized approach to healthcare.
1. Personalized Health Insights:
One of the key contributions of AI in patient engagement is its ability to provide personalized health insights. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of patient data, considering individual health history, genetic factors, and lifestyle choices. This allows for the creation of tailored recommendations, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their health. Personalized insights contribute to a sense of ownership over one’s health, encouraging patients to actively participate in their care.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring:
AI-enabled remote patient monitoring solutions are transforming how patients and healthcare providers interact. Wearable devices equipped with AI can continuously collect and analyze health data, offering real-time updates to both patients and providers. This not only facilitates early intervention in case of emerging health issues but also keeps patients connected to their care plans outside traditional healthcare settings. Remote patient monitoring enhances patient engagement by providing a more comprehensive view of their health on an ongoing basis.
3. Virtual Health Assistants:
AI-driven virtual health assistants are becoming valuable companions in patients’ healthcare journeys. These intelligent assistants provide instant access to information, answer queries, and offer guidance on medication schedules, lifestyle modifications, and post-treatment care. By creating a virtual bridge between patients and healthcare resources, AI-driven assistants promote continuous engagement and enable patients to stay informed and proactive about their health.
4. Predictive Health Analytics:
AI’s predictive analytics capabilities contribute to patient engagement by anticipating potential health risks. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, AI can predict the likelihood of specific health events. This foresight empowers patients to take preventive measures, make lifestyle adjustments, and adhere to recommended treatments, ultimately reducing the risk of unplanned hospital visits and improving overall health outcomes.
5. Gamification for Health:
Innovative AI applications introduce elements of gamification into healthcare, turning health management into an engaging experience. Gamified platforms leverage AI to create challenges, set goals, and reward positive health behaviors. This approach not only makes health management more enjoyable but also motivates patients to actively participate in their wellness journey.
Conclusion:
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on enhancing patient engagement in healthcare is becoming increasingly apparent. From personalized health insights to virtual health assistants and gamified health management, AI is empowering patients with knowledge, motivation, and tools to actively participate in their healthcare. This collaborative approach between AI and patient engagement not only improves individual health outcomes but also contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. As we navigate the future of healthcare, the synergy between AI and patient engagement promises a more personalized, proactive, and patient-centric model of care.
Introducing HealthScan – Experience the future of healthcare with our innovative app designed to foster a seamless biometric connection between healthcare providers and their patients..